Iran – Israel on the Brink of a “Safe Abyss”
when is it no longer “safe” ?? A free article by Elijah Magnier. Presciently published 2-3 days PRIOR to the Iranian retaliation. Iran moved from Patience to direct Power. Henceforth, there will be consequences for Zio-USUK, as in Novorossiya!
By Elijah J Magnier on 11/04/2024.
In a calculated move of retaliation, Iran has decided to respond to Israel’s actions by earmarking several targets from its extensive list for initial and, if deemed necessary, subsequent more destructive reprisals. Reliable sources reveal that Iran’s strategic planning includes the Israeli Chief of Staff’s headquarters among the range of potential targets. This decision is a direct consequence of Israel’s targeted assassinations of Iranian generals on Monday, 1 April 2024, which targeted the Iranian diplomatic consulate in Damascus, Syria. This attack destroyed the consulate and the death of seven senior Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) officers, including a brigadier general and general, his second in command. In the light of these events, Iran has vowed to retaliate.
Hezbollah, an ally of Iran, proposed a joint attack on Israel. However, reliable Iranian sources report that Sayyed Ali Khamenei, Iran’s Supreme Leader, rejected the proposal. Sayyed Khamenei’s refusal is based on a desire to prevent harm to Iran’s allies and a belief that retaliation should be an exclusively Iranian response, especially after the attack on its diplomatic consulate. The purpose of Iran’s planned retaliation is not necessarily to effectively harm Israel by destroying its diplomatic mission but to send a warning. This serves as a deterrent message to Israel and the international community to refrain from similar actions in the future. Iran’s strategy is not aimed at escalating the situation into a wider conflict unless Israel retaliates. Instead, Iran is trying to navigate out of the position it has been placed in by Israel’s actions against its diplomatically and legally protected consulate in Syria.
Israel’s conduct violates essential norms protecting the inviolability of diplomatic premises and representatives, as enshrined in the Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961), the Convention on Consular Relations (1963), and the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Crimes against Internationally Protected Persons, including Diplomatic Agents (1973).
Invoking Article 51 of the United Nations Charter, which sanctions the right of individual or collective self-defence in response to an armed attack against a UN member state, Iran is in a position to retaliate against Israel without the option of restraint. This stance is based on the need to protect its diplomatic missions around the world. Iran has notified the United States of its intention to retaliate by international legal frameworks while at the same time preparing for possible further escalation by Israel by preparing additional countermeasures in the event of significant Israeli retaliation.
Delaying a retaliatory strike does not put Iran at a disadvantage, as strategic depth and patience define its approach to conflict. This stance emphasises that time serves Iran’s interests by allowing it to respond to any aggression in a calculated manner and by draining Israel’s resources and nerves in anticipation of Iranian retaliation. The notion that the explicit intent of a “damaging strike” would typically come from the “Axis of Resistance” that aims to underscore a strategy of surprise and direct engagement. On the other hand, Iran’s primary goal isn’t just tit-for-tat but to prevent future provocations and maintain established limits of engagement.
Iran’s decision-making process is not hasty or impulsive but deliberate and methodical. It is based on a thorough assessment of the immediate facts, strategic evaluations, and broader implications on the regional and international stage. This approach instils confidence, as it shows that Iran’s actions are not driven by the clamour of public opinion on social media but by a complete understanding of the potential consequences.
The leadership’s emphasis on strengthening the resilience of the Iranian people, increasing national enthusiasm, and reinforcing ideological cohesion is not just a prelude to military action but a testament to Iran’s commitment to its citizens. The Iranian leadership considers this internal fortification more important than the act of retaliation itself, highlighting the depth of their commitment.
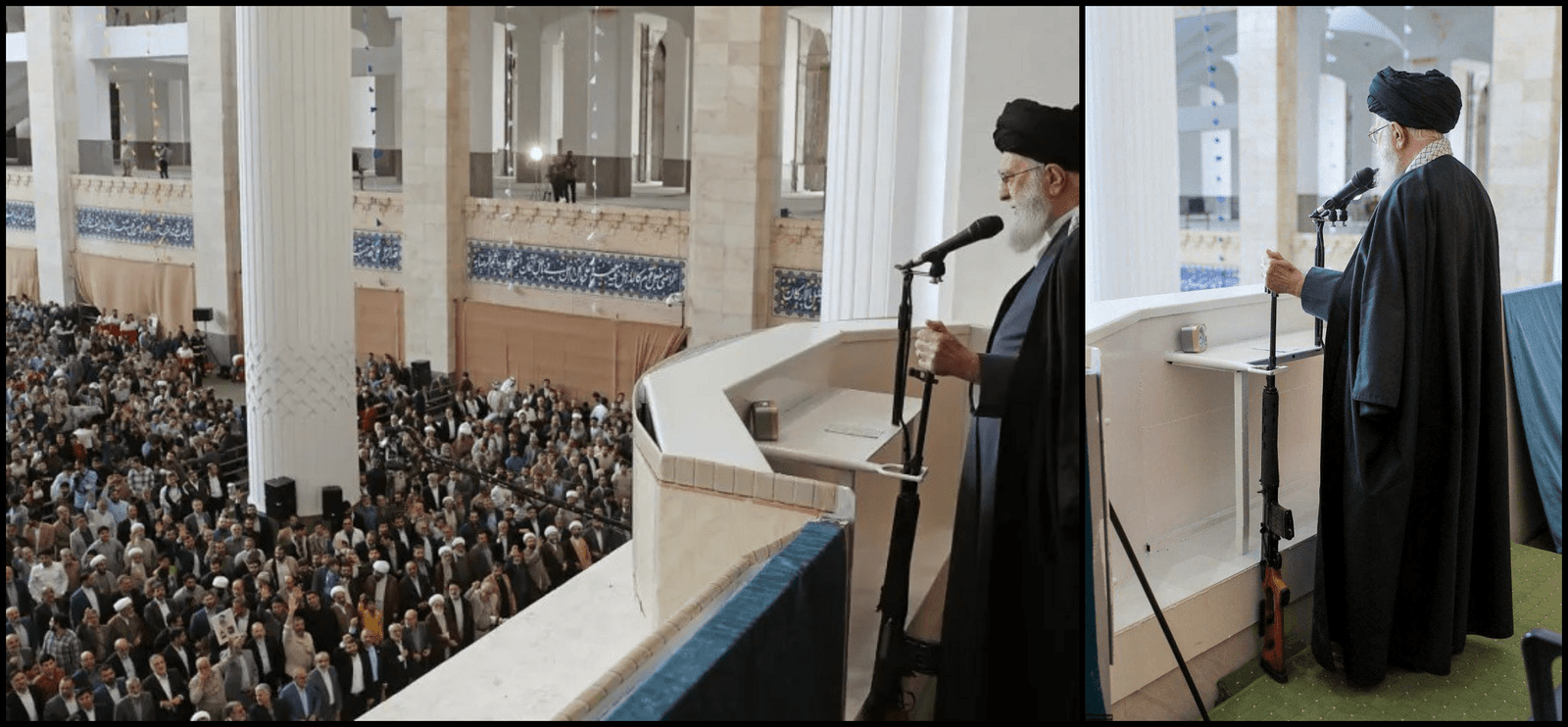
The symbolic gesture of Sayyed Khamenei appearing with a Russian Dragunov semi-automatic sniper rifle during the Eid al-Fitr sermon, an action usually reserved for Friday sermons, is a deliberate display of readiness for conflict. This act is not just a message of defensiveness but a declaration of Iran’s readiness and resolve, reinforcing its strategic position and ideological steadfastness.
In sum, Iran is a nation that approaches the prospect of conflict with caution, strategic planning and a deep-seated commitment to preserving its sovereignty and principles rather than being swayed by external pressures or immediate provocations.

‘Operation Faithful Promise’ written in a red rocket
Iran’s measures
Iran has upgraded security measures around more than 91 Iranian sites deemed ‘sensitive’ as a defensive measure. These measures included its infrastructure, nuclear facilities and military installations, underlining its comprehensive approach to hardening its critical infrastructure against potential Israeli threats. This strategy appears to mirror tactics seen elsewhere, including by Israel and highlights a trend towards multi-layered defence systems that combine physical interception measures with electronic warfare capabilities.
Indeed, Iran’s deployment of anti-aircraft and interceptor missiles at critical sites, including nuclear facilities and military bases, represents a direct approach to countering air threats such as human-crewed aircraft, drones and missiles. These systems range from short-range air defence (SHORAD) systems designed to engage targets at lower altitudes to advanced long-range missile defence systems capable of intercepting high-altitude threats and fighter jets.
Furthermore, the Iranian deployment of GPS jamming systems throughout Iran indicates a significant emphasis on countering precision-guided munitions and navigation-dependent drones and missiles. By degrading the accuracy of GPS-guided weapons, Iran aims to reduce the effectiveness of potential attacks on its territory, particularly on sites critical to its national security and infrastructure. GPS jamming can create a defensive buffer, making planning and executing air strikes more challenging.
By publicly demonstrating the enhancement of its defensive capabilities, Iran seeks to deter potential adversaries from considering direct attacks by projecting a willingness to defend its critical assets. This move reflects the ongoing technology race in military capabilities, where corresponding improvements match advances in offensive weapon systems in defensive technologies. Also, strengthening Iran’s defensive posture may have implications for regional security dynamics, potentially affecting the calculus of NATO, Israel and other regional actors regarding their security strategies and policies.
Using GPS jamming on a national scale highlights the growing importance of electronic warfare in modern defence strategies. It not only complicates adversaries’ operational environment but also represents an investment in non-kinetic means of warfare.

(L): Il Papa kisses the Ring ; (R): Christian Zionist former Vice Prez Pence at Christians United for Israel (CUFI)
Israel measures
Israel’s approach to missile defence is indeed multi-layered and highly sophisticated, designed to counter a wide range of threats from short-range rockets to medium-range ballistic missiles. This defence strategy includes several key components to provide a comprehensive shield. In addition, the involvement of NATO, particularly with naval assets equipped with missile interceptors, provides an international dimension to regional missile defence efforts.
Israel’s missile defence architecture consists of several layers, each designed to engage different types of threats at various ranges and altitudes:
Iron Dome: Primarily aimed at intercepting short-range rockets and artillery shells. It is known to have been effective in intercepting projectiles from Gaza.
David’s Sling: Targets medium- to long-range rockets and cruise missiles, filling the gap between the Iron Dome and Arrow systems.
Arrow 2 and Arrow 3 systems: Designed to intercept ballistic missiles at high altitudes, including outside the Earth’s atmosphere, providing a last line of defence against long-range threats.
Role of Patriot Missiles in Israel’s Air Defense: Israel’s inclusion of the Patriot missile system in its air defence arsenal is a significant component of its multi-layered defence strategy aimed at countering various aerial threats. Initially developed by the United States, the Patriot missile system is designed to detect, track, and engage incoming ballistic missiles at high altitudes, as well as aircraft and drones.
GPS jamming and non-GPS-guided threats: The Israeli army uses GPS jamming to mitigate the threat posed by precision-guided munitions, including missiles and drones that rely on GPS for navigation. By jamming or spoofing GPS signals, defenders can degrade the accuracy of incoming threats, potentially diverting them from their intended targets. However, as noted above, not all missiles and drones deployed by Iran and its allies rely on GPS for guidance. Many systems may use alternative navigation methods, such as inertial guidance, which uses gyroscopes and accelerometers to maintain a course without external references. Others may use Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM) or optical or radar-based homing technologies that are not susceptible to GPS jamming.
Furthermore, NATO’s deployment of missile interceptors around Israel and in the Red Sea and the Mediterranean demonstrates a high level of cooperation and commitment to Israel’s defence. These ships will likely be equipped with Aegis combat systems capable of tracking and shooting down enemy missiles and aircraft, enhancing Israel’s national missile defence capabilities.
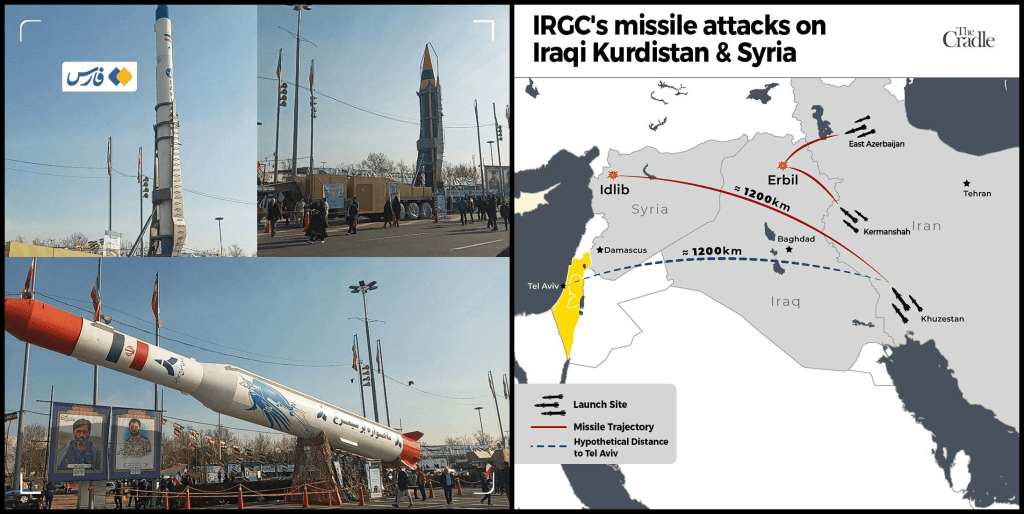
(L): Display of satellite rockets, Khorramshahr missile, and Qiyam-1 missile in the national day parade, 11.02.2024 ; (R): Iran’s missile strikes against Mossad & terrorist targets in Iraq and Syria, 15.01.2024
Countermeasures
However, missile guidance systems, especially those used by countries such as Iran and its allies (Hezbollah, Iraqi Resistance), have evolved to incorporate a variety of technologies aimed at improving accuracy and reliability while evading countermeasures. One such technology is using gyroscopes in the missile’s guidance system. Let’s look at the basics of how these systems work, their advantages and their potential limitations.
A gyroscope in a missile guidance system performs a critical function: it provides inertial navigation data. This means that it can measure and maintain the orientation and angular velocity of the missile without external references. It tells the rocket whether it has rolled, pitched or yawed during flight and by how much.
How it works? A gyroscope maintains its orientation using the principle of angular momentum. In the context of missile guidance, it can provide a stable reference that indicates the missile’s orientation relative to the Earth’s surface. By integrating data from gyroscopes with accelerometers (which measure acceleration), the missile’s inertial navigation system (INS) can calculate its position, orientation and velocity without needing external references such as GPS.
One of the main advantages of using a gyroscopic guidance system is its independence from external signals such as GPS. This makes the missile less susceptible to jamming and spoofing techniques, which are common electronic countermeasures used to disrupt the guidance of GPS-guided weapons. Relying on an internal guidance system allows the missile to be guided to its target even in environments where GPS signals are compromised.
Gyroscopes make missiles more resistant to jamming and spoofing. They do not rely on external updates and can operate in GPS-denied environments. When combined with accelerometers in an INS, gyroscopes can provide precise navigation capabilities.
However, Inertial navigation systems, including gyroscopes, can accumulate errors over time. The longer the missile is in flight, the greater the potential error in its calculated position. Thus, implementing a robust gyroscopic guidance system can be complex and expensive compared to simpler GPS-based systems. Still, it is necessary when facing an advanced enemy with a GPS jamming system. Gyroscopic missile guidance systems offer significant advantages regarding autonomy and resistance to electronic countermeasures, making them particularly useful for countries such as Iran that can anticipate GPS jamming techniques.

Legal approach
The attack on the consulate of a nation, which caused both material damage and fatalities, is a severe violation of international norms, in particular the 1961 Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, which stipulates the inviolability of diplomatic premises and the protection of diplomatic personnel. In response, Iran lodged a formal protest with the United Nations, highlighting the international condemnation by entities such as the United Arab Emirates, the members of the Gulf Cooperation Council (except Bahrain), Russia and China, all of which emphasised the sanctity of diplomatic premises and condemned the violation of these principles.
The collective condemnation by the 121 countries of the Non-Aligned Movement demonstrates global solidarity with Iran and highlights the significant geopolitical implications of disregarding diplomatic norms. Yet the Western response has been muted, with minimal public condemnation, reflecting a polarised global perspective on the incident.
Iran’s efforts to rally international support to isolate Israel diplomatically, coupled with Israeli Minister Benny Gantz’s call for a coalition against Iran, reflect the complex global dynamics at play. Iran is criticising the United States, Britain and France for not supporting a UN Security Council condemnation of the Israeli attack on its consulate in Damascus, which Iran blames on US-supplied weapons. This position is being portrayed as a tacit endorsement of the aggression, risking further instability in West Asia. Iran asserts its right to seek legal redress and retaliation under international law for this affront.
In solidarity, Ansar Allah in Yemen and Hezbollah in Lebanon expressed their unwavering support for Iran and condemned the attack on the consulate. The support of Iran’s powerful allies was manifested during Iranian Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian’s talks in Muscat, Oman, which focused on sending the right message and soft warning to the US administration to remain neutral.
Since 7 October, the United States has already sent four indirect messages to Iran, urging Tehran to remain in control and not to be provoked into joining Netanyahu’s conflict. The messages stressed that the US administration would do everything in its power to contain the conflict. However, Iran perceives that the US has not lived up to its commitments and points to Israel’s actions, which have further antagonised Iran, including the destruction of its consulate in Damascus, as evidence of this failure.
Iran is aware that the US will not abandon Israel, just as Israel and the US know that Iran’s main allies in Lebanon, Syria, Iraq and Yemen will stand by it. This mutual recognition is what led Israel’s Prime Minister, Benjamin Netanyahu, to believe that he could carry out a strike on the Iranian consulate with impunity and expect no retaliation from Iran.
The US is limited to intercepting missiles and drones aimed at Israel and using its diplomatic clout to defuse tensions and prevent Israel from escalating the situation, given the potential for full-scale conflict. The prospect of the US becoming embroiled in a Middle East conflict, especially one it could start but find difficult to end, is particularly unappealing as President Joe Biden faces a presidential election in two months. The US administration, already unhappy with Israel’s conduct in the Gaza conflict, is putting pressure on Netanyahu to cease hostilities and facilitate humanitarian aid. As a result, there is little appetite for escalation, which could only benefit Netanyahu by prolonging his tenure and aiding his domestic political survival while significantly undermining Biden’s re-election ambitions. This precarious situation encourages all parties to remain vigilant and avoid Netanyahu’s potentially dangerous strategies, especially as he faces declining domestic and regional support due to various failures.











